Bacterial Spot of Tomato
Return to Diseases
Bacterial spot (Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria) leaf lesions are small, circular, and brown in color; spots infrequently have a yellow halo. Lesions can coalesce and form large blighted (suddenly dead) areas in the plant canopy. Defoliation may occur in severe cases. Differentiating leaf symptoms of bacterial spot and bacterial speck can be difficult; however, bacterial spot lesions tend to have a wet or greasy appearance. On green fruit, bacterial spot lesions begin as raised blisters and reach a maximum size of about ¼ inch. Fruit lesions tend to have a scabby appearance and can be slightly raised or depressed in the center. Disease is most likely to occur when conditions are warm and humid or rainy.
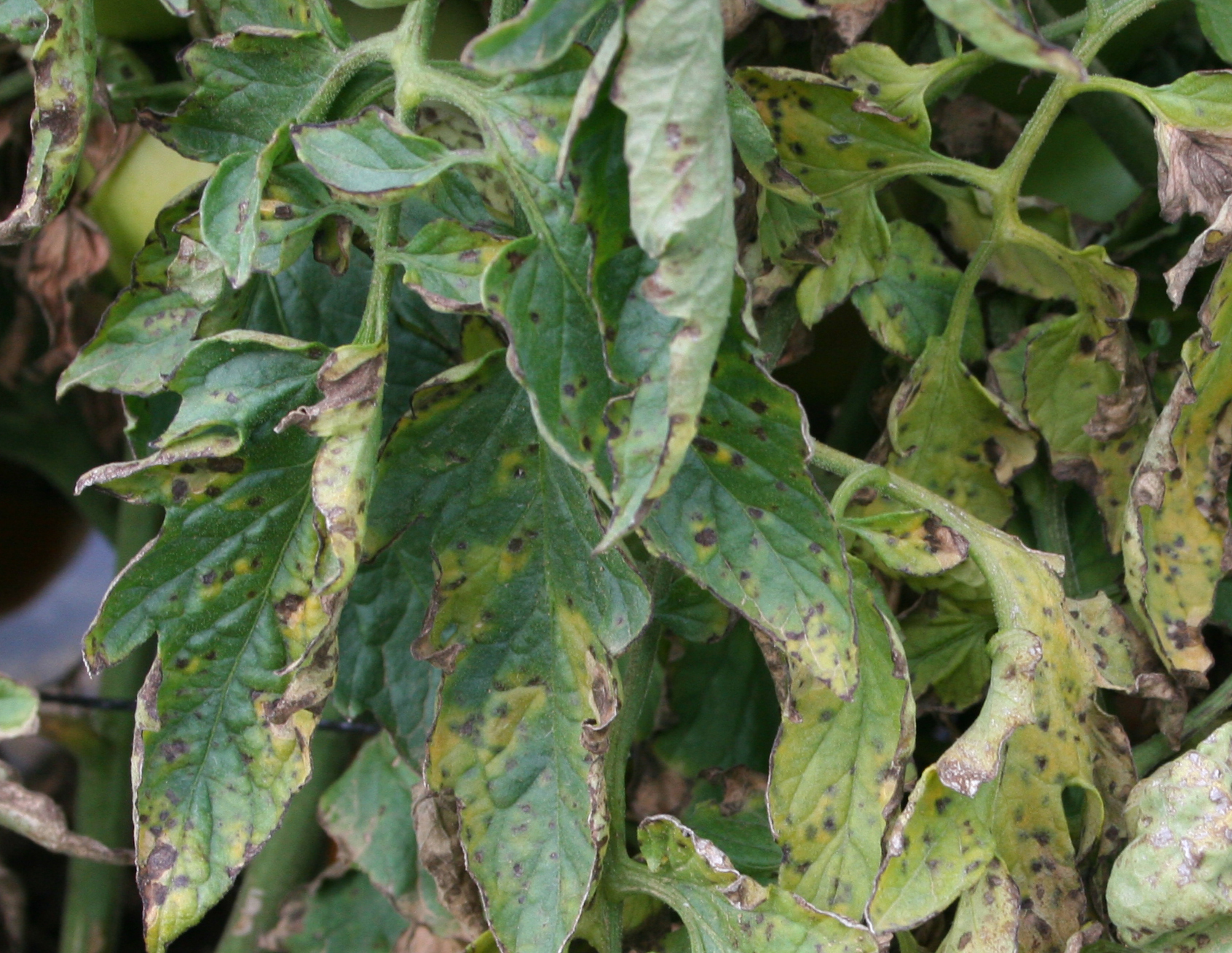

Bacterial spot on leaf.
(Photo: Kenny Seebold, University of Kentucky)
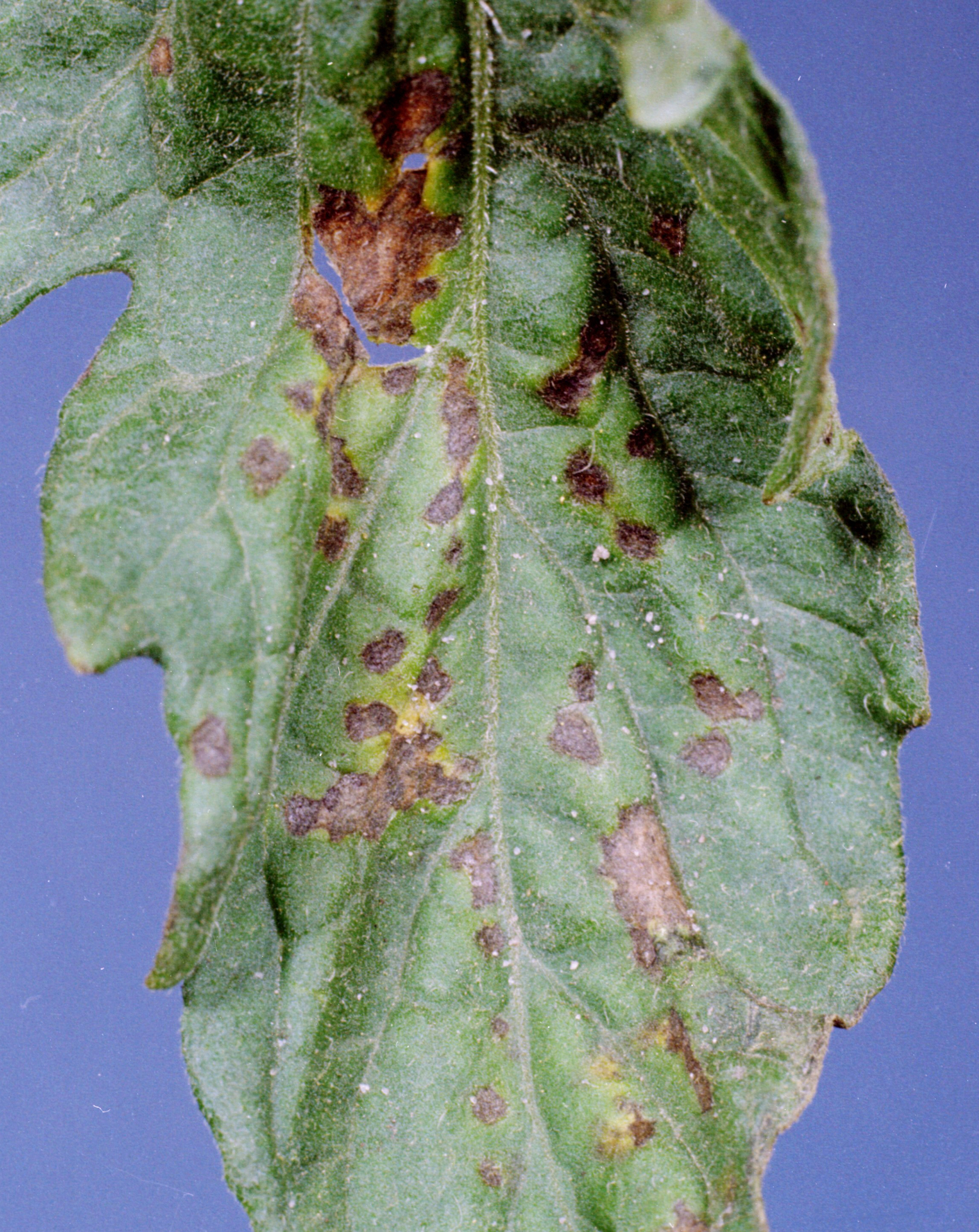

Bacterial spot on leaf.
(Photo: USDA Cooperative Extension Slide Series, Clemson University, Bugwood.org)
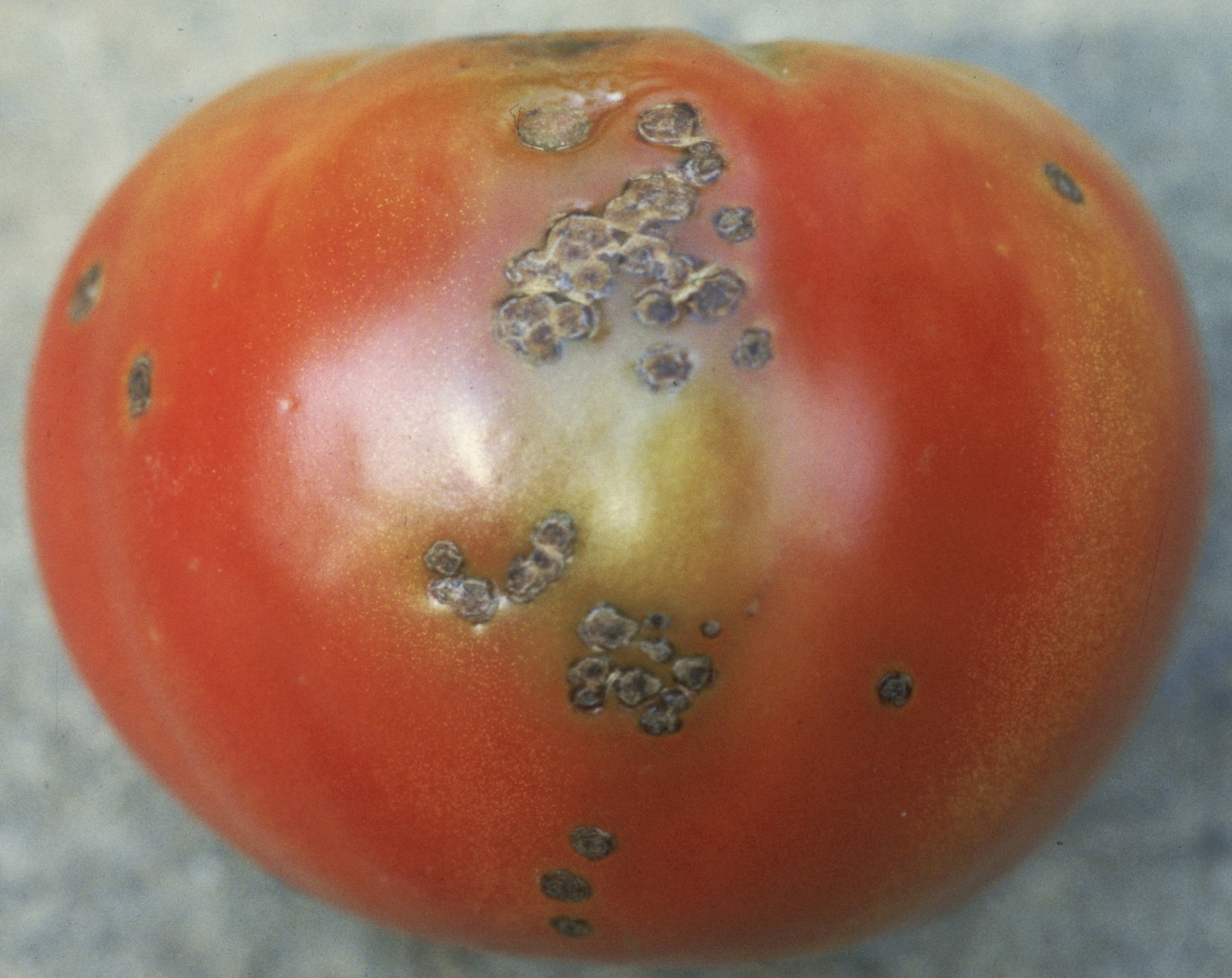
Bacterial spot on fruit.
(Photo: Mary Ann Hansen, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Bugwood.org)
Management:
- Plant pathogen-free seed and transplants
- Disinfect tools and implements
- Avoid overhead irrigation or working with plants when they are wet
- Apply a protectant bactericide
- Promptly remove and destroy diseased plant material
- Rotate with non-host crops
- Destroy crop residues after harvest
- Deep plow to bury residual inoculum
